Bandhara Irrigation: An Effective Technique for Small-Scale Agriculture

This post was originally published on this site
Table of Contents
1. Bandhara Irrigation: A Classic Technique for Small-Scale Agriculture

✔ Bandhara irrigation is a definitive irrigation technique typically employed in India, significantly in the western states of Maharashtra and Gujarat. It is also known as “tank irrigation” or “percolation tank irrigation.
✔ It is a nominal irrigation system that operates slight earthen dams or weirs built across streamlets or rivers to redirect and reserve water for agricultural ambitions. The Bandhara irrigation approach is utilized for relatively undersized areas, typically up to rare hectares (around 500-2000 square meters).
✔ A small network is constructed across a small creek or river that acts as an obstacle to increasing the water level on the upper flank of the stream. The water is then shifted straight for Irrigation via a canal. It enables the Irrigation of spaces encircling the structure.
2. Types of Bandhara Irrigation:
I. Solid Bandhara
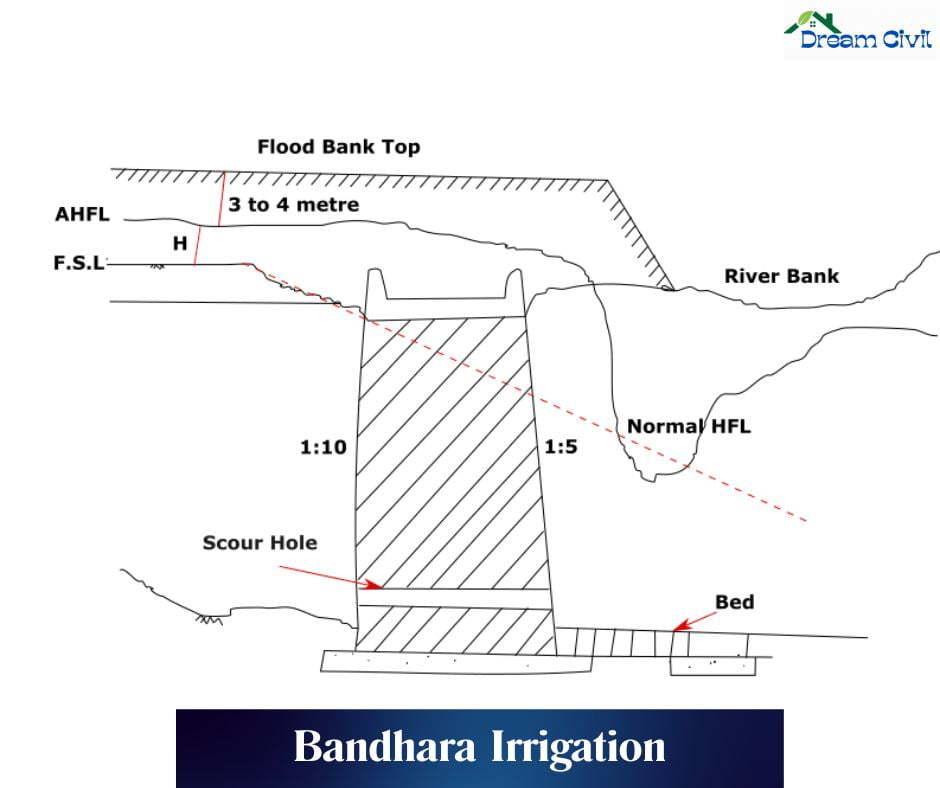
✔ Bandharas are designs that supplement the water level upstream without afflux. They consist of masonry ports with tracks where syringes are positioned. Solid bandhara is 2.5m to 3.5m high, with shutters or without shutters (1.5m to 2.5m). They perform as weirs and stock water center-monsoon.
II. Open Bandhara
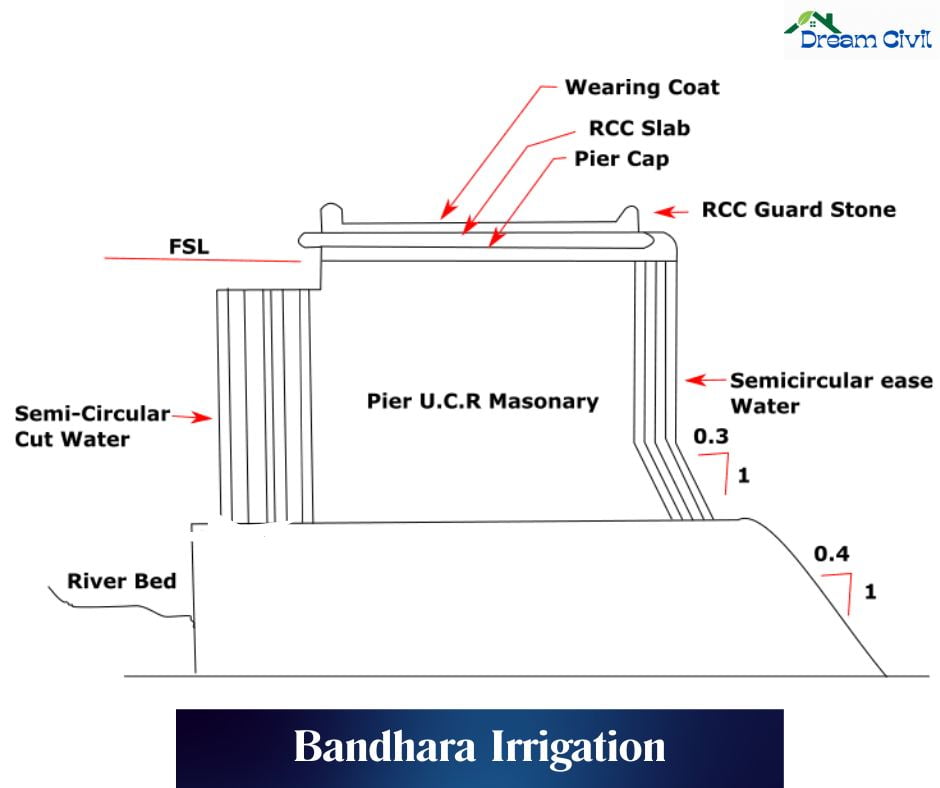
✔ Bandhara dams are built in Kolhapur to increase water levels and shift water through canals. They consist of ports with syringes that can be counted or released to accommodate the peak of the weir. Needles are 15cm elevated, 5cm wide, and 2m lengthy and should be substituted every five years.
3. Fundamental Elements of Bandhara Irrigation:

-
Remote-scale Irrigation: Bandhara irrigation is appropriate for irrigating slightly more extensive areas, varying from a rare hectare to approximately 500 hectares.
-
Avocation of water: A bandhara shifts water from a creek into a canal to flush or rinse surrounding areas.
-
Water storehouse: Bandharas can even act as water storehouse waterholes, delivering irrigation water during dry durations.
-
Groundwater recharge and percolation: Bandharas can sweeten groundwater recharge by permitting reserved water to bleed into the setting, which restocks groundwater storage and improves water availability.
4. Advantages of Bandhara Irrigation
✔ Highly economical irrigation system.
✔ Very Efficient and effective utilization of local water resources.
✔ Irrigation will be adequate with this weir due to the consolidated area in irrigation deficiency.
✔ The canal near the weir has a minor water flop and additional intensive Irrigation.
✔ Small catchment area surrounded by weir so waste will be operated entirely.
✔ Simple walls function as bandhara to reserve water.
5. Limitations of Bandhara Irrigation
✔ Small irrigation potential
✔ Dependency on rainfall
✔ Possibility for siltation
6. Selection of a site for Bandhara:
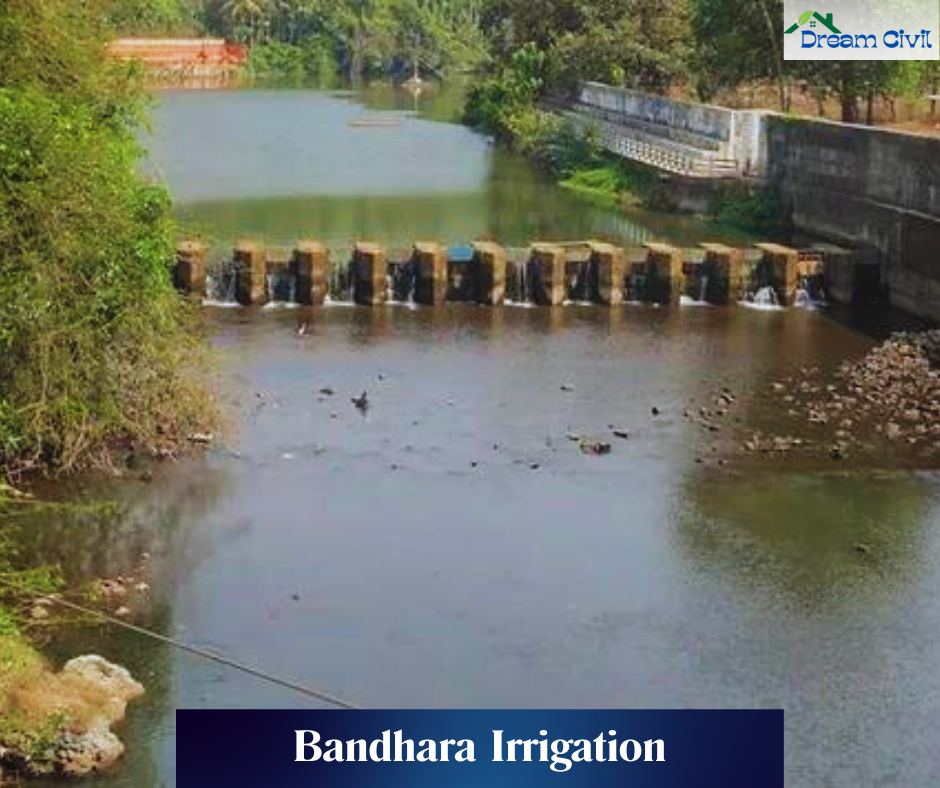

- Proximity: The site should be close to the irrigated space for effectiveness and efficiency.
- Water Junction: Below the convergence of creeks for compatible water supply.
- Perennial Source: Build an annual river for a trustworthy water supply.
- Foundation Quality: Assure an excellent footing for the bandhara structure.
- Economical Construction: Underline cost-effectiveness.
- Upstream Location: Upstream of a vertical pitch for effortless water flow.
- Direct River Access: Immediate practice for canal construction on both flanks.
- Local Surroundings: Within a 5km radius of the irrigated location.
- Avoid Deep Excavation: Underestimate the in-depth hole for the canal edifice.
- Consideration for Agriculture: Authorize undersized farmed areas to be immersed upstream.
- Preserve Natural Drainage: Secure channels don’t block natural drainage routes.
7. Bandhara irrigation scheme
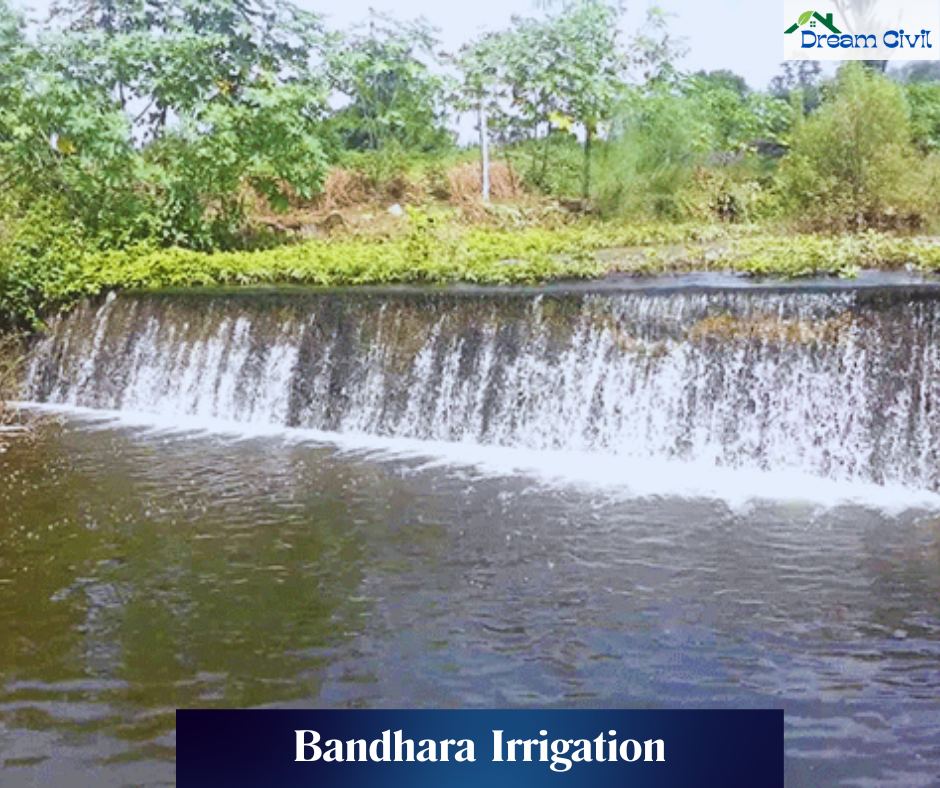

✔ The Bandhara irrigation scheme is an outstanding system utilized in some regions of Maharashtra for nominal irrigation ideals. In this system, a weir is constructed upstream across a little river or creek using avocation weir walls.
✔ The weir is assembled with brick, stone masonry, or concrete, enabling water delivery to a remote area of about 5km via a small canal.
✔ Canals carry water for Irrigation from both flanks of the bank upstream. The Bandhara irrigation scheme is a cost-effective strategy for irrigating these small rivers.


Responses