Obligatory Points in Highway Alignment : With 2 Types
This post was originally published on this site
Table of Contents
1. What are Obligatory Points?
Obligatory Points refer to the control points that govern highway alignment. These points determine where the alignment should pass and where the alignment should not pass.
2. Explain the types of Obligatory Points.
The obligatory points are classified into two types.
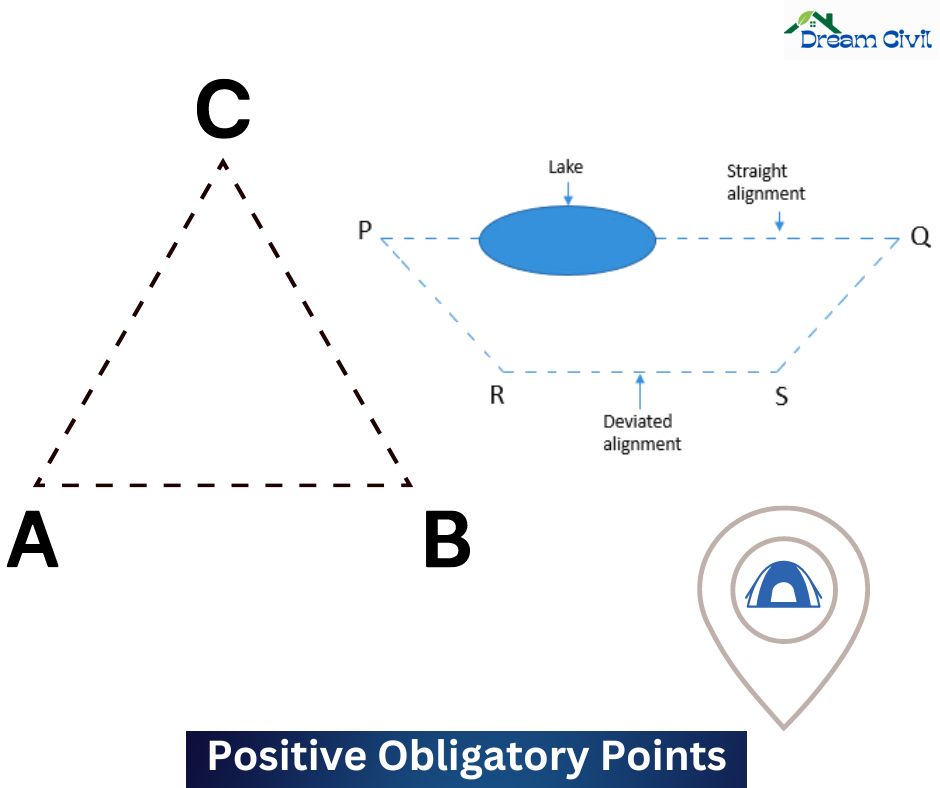
1. Positive Obligatory Points:
Positive obligatory points are those points through which the alignment should pass.
a. Existing Road: The alignment that should be fixed where the newly constructed road connections to the existing road. It decreases the cost of construction.
b. Intermediate Town: If there is the chance of a linear road between points A and B and there lies a middle town at C, as shown, then the route requires connecting the intermediate village to reduce the change in highway alignment.
c. Bridge site/Existing Bridge: The preference of the bridge site concerns multiple characteristics and is concluded where the river path is identical throughout the year. The road connecting with the bridge must not be curved, and the highway alignment may be modified to enclose the bridge in the road portion. The road alignment should clip the river at 90 Degrees, identical to the Railway lane.
d. Mountain: If the alignment departs through the mountain, peeking at the best options, either building the tunnel or reaching around the hills, is instructed. A mountain pass may be a reasonable option when the road has to strike a row of hills. The option picking relies on topography, site requirements, and construction and operation costs.
Read Also:
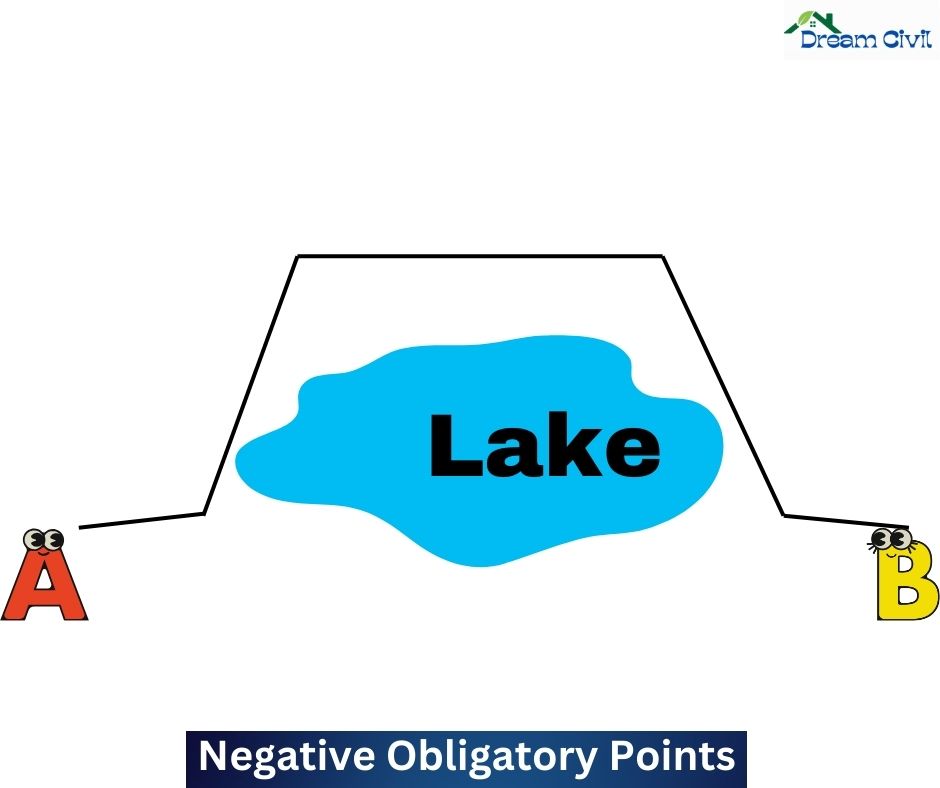
2. Negative Obligatory Points:
Negative Obligatory Points refers to points the alignment should not pass.
i. Valleys, ponds, and marshy land require to be bypassed.
ii. Religious places are connected with human sentiment, so they cannot be beaten to correct the road alignment.
iii. Costly structures present in the form of alignment should be regarded, and the road alignment should be specified so that it won’t eliminate those costly structures, as the compensation significance for such structures will be higher.
iv. Preservation areas and limited zones.
v. Densely populated area.
vi. The road should not be within the border of the country.



Responses